Thalassemia is a blood disorder that leads to a decrease of hemoglobin production. Our bodies need hemoglobin because it helps red blood cells carry oxygen and low hemoglobin results in anemia. Hemoglobin is a protein that consists of two chains an alpha and a beta protein chain and several genetic mutations can affect these chains. There are 4 genes that affect that alpha-globulin chain in hemoglobin and 2 that affect the beta-globulin chain in hemoglobin
Thalassemia meaning
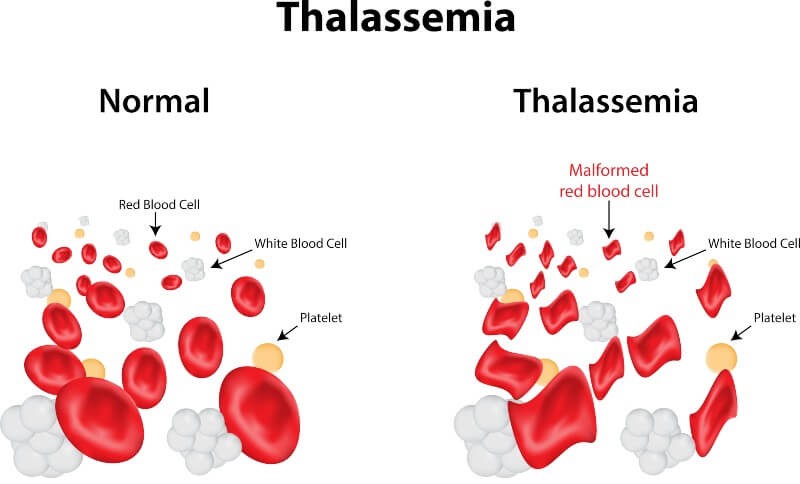
Thalassemia is a genetic blood disease that leads to a reduction of hemoglobin levels in blood. Hemoglobin is used by red blood cells to carry and deliver oxygen to organs. Clinical severity varies greatly depending on which genetic mutation underlies the disease. Symptoms can be mild like fatigue and some shortness of breath and go as far as life threatening anemia.
One of the severe types of thalassemia involving a mutation in 2 of the beta-chains of hemoglobin is also called Mediterranean Anemia due to its higher frequency around the Mediterranean Sea.
Thalassemia symptoms
Symptoms of thalassemia differ from one person to another;
Thalassemia (all forms) are inherited in a Mendelian recessive manner. This means you can be a carrier with no or very mild symptoms or have more severe ones depending on the type of mutation and the chain it affects.
1- Symptoms of the disease in people with mild illness are simple: they show signs and symptoms of simple anemia such as pallor and fatigue.
2- Symptoms of those with medium anemia are pallor, fatigue, shortness of breath, palpitations
3- Major thalassemia symptoms usually the type also called Mediterranean Anemia:
- Pallor of skin.
- Anorexia.
- Dark urine
- Slow growth and delayed puberty.
- Jaundice: It is yellowing the skin or the whites of the eyes.
- Enlarged spleen, liver, or heart.
- Bone problems, especially facial bones
Thalassemia in children
For children with thalassemia the onset of noticeable symptoms varies according to the type of thalassemia they have. In newborns with a specific beta type (Mediterranean Anemia), the symptoms often appear six months after birth, less severe types may not notice any symptoms until after late childhood, or even adolescence.
Thalassemia causes
Thalassemia is caused by mutations in the DNA of cells responsible for the production of hemoglobin, a substance in red blood cells responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body. Thalassemia-related mutations are passed down from parents to children.
Hemoglobin molecules consist of chains called alpha-chains and beta-chains. A mutation in the DNA of genes responsible for the produce of hemoglobin change the structure or make these chains absent.
Alpha thalassemia has 4 genes that affect its chains and Beta thalassemia has 2 genes affecting its chains. Thus,
Types of thalassemia
There are two types of thalassemia:
Alpha Thalassemia
The severity of thalassemia depends on the number of genetic mutations inherited from parents. The more the genes affecting the chains are absent the more severe the symptoms are. Alpha thalassemia’s type and severity depend on the number of genes (1-4) that are absent. There are 4 types of alpha thalassemia
- Alpha thalassemia silent carrier: one gene is absent or damaged these patients usually have no symptoms and blood tests apart from some smaller red blood cells are usually normal.
- Alpha thalassemia carrier, 2 absent genes these patients usually have a mild anemia
- Hemoglobin H disease: 3 absent genes leaving only one normal gene, these patients usually have moderate to severe anemia that can get worse with certain medication or when having a fever. Throughout life several blood transfusions might be needed
- Alpha thalassemia major: All 4 genes responsible for the alpha-chains are missing. Children with these mutations usually die before or soon after birth.
Beta Thalassemia
The severity of thalassemia depends on mutations in the 2 genes responsible for the Beta-chain of the hemoglobin molecule in blood. Beta thalassemia can be divided into 3 types;
- Beta thalassemia minor: These people are usually asymptomatic and not know they have a form of thalassemia. Occasionally they have a mild anemia.
- Beta thalassemia intermediate: patients are anemic, pale and experience overall fatigue.
- Beta thalassemia major (Mediterranean anemia); both genes for B-globulin chains in hemoglobin are absent. Children before the age of 2 are usually diagnosed due to severe anemia they will require lifelong blood transfusions and medical care.
Thalassemia treatment
Treatment of thalassemia symptoms vary according to the type and severity of the thalassemia Although there are many experimental thalassemia treatments, none of them are working as a definitive treatment so far especially in the major forms of Alpha and Beta thalassemia. Symptomatic treatments include,
1- Blood transfusion
Blood transfusion is the first line of treatment in the treatment of Thalassemia in its major forms depending on the severity of the cases blood is transferred to the patient from twice a month to maybe quarterly.
2- Food supplements
Thalassemia patients usually need food supplements like folic acid and iron because they are important for red blood cell production.
Thalassemia Recovery
recovery from thalassemia is not definitive but is treated symptomatically this is more difficult for advanced cases.
Many people wonder if thalassemia is a serious condition?
Answer is yes, this disease can be serious especially if you have one of the severe forms of it. Regular checkups with your doctor and follow up are an essential part of your treatment plan.
Is thalassemia dangerous?
Many people wonder if thalassemia is serious. Yes, this disease can be serious if you do not follow up with your doctor regularly and take convenient treatments for the condition. Complications that may occur as a result of thalassemia are:
- Myocardial insufficiency that may lead to death.
- Liver disorders.
- Endocrine disorders.
Prevent passing thalassemia on to your children
Bedaya can help you to not pass thalassemia on to your offspring!
Alpha thalassemia, and beta-thalassemia with their subdivisions affect one thousand children of the 1.5 million children born annually in Egypt. We at Bedaya have the means to screen both parents for the mutation predicting the chances they could pass on thalassemia to their offspring.
For those where both parents are carriers Bedaya Hospital offers an even better solution! With the new preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy PGT-M available at Bedaya Hospital embryos obtained through an IVF/ICSI cycle can be diagnosed and so only the embryos without the faulty genes are put back guaranteeing your children won’t inherit the faulty genes causing the thalassemia.