A common condition in girls and women in reproductive (menstruating) years. 70-80% of women will develop them at some point in their lives. Fibroids are benign tumors that develop in the uterus and consist of muscle and fibrous tissue. Fibroids do not spread to other places in the body.
Uterine fibroids are classified according to their location in the uterus into 4 types.
- Intramural fibroids these grow within the muscular uterine wall
- Submucosal fibroids bulge into the uterine cavity
- Subserous fibroids grow on the outer wall of your uterus (serosa).
- Pedunculated fibroids are subserous fibroids that develop a stem
What are uterine fibroids?
Uterine Fibroids are the most common tumors in the female reproductive system, occurring in about 40% of women between the ages of 30 – 50. They are benign tumors formed in the muscular layer of the uterus and may appear as a single tumor or several tumors. Their size can grow up to 25 cm in size, their symptoms vary correlating with the type, location, and size. It is usually accompanied by vaginal bleeding if involving the inner uterine lining (endometrium) and according to its size it can cause no symptoms at all, to some discomfort, to severe abdominal pain.
There is no known cause of these tumors, but they may be related to an increase in the proportion of estrogen.
Symptoms of uterine fibroid
Symptoms of uterine fibroid vary depending on the location of the mass, the size of the fibroid, the extent of its effect on the surrounding tissues as well as the general health and history of the patient like previous uterine surgeries, thrombophilia profile etc. This all sounds a bit overwhelming but really fibroids mostly don’t cause any symptoms and are coincidental findings during a routine checkup or during a pregnancy ultrasound.
Uterine bleeding is the most common symptom associated with fibroids and may show as:
1- An increase in the number of menstruating days. Menstruation lasts more than 8 days
2- Increase of menstrual blood flow (quantity)
3- Increased uterine bleeding may lead to anemia. Symptoms of anemia;
- - A decrease in hemoglobin
- - An increase in heart rate accompanied by shortness of breath
Observing such changes and noting there is a problem is very personal every woman knows the nature of her menstrual cycle and it can each’s normal can be very different from another.
4- On average, women lose 30-40ml of blood during their menstrual cycle. When having a fibroid that affects the endometrium lining this amount can increase.to 50-80 ml per month.
What causes uterine fibroids to grow?
The definite causes of uterine fibroids remain unclear, although many factors have been observed that increase the chances their development.
Genetic mutations
The hormones estrogen and progesterone are responsible for preparing the uterine lining to receive a fertilized egg and for maintaining pregnancy. These hormones thus also through some altered genetic mutation in their receptors cause the growth of fibroids.
Fibroids mainly grow in a woman’s fertile years when estrogen and progesterone are secreted in high levels after menopause their incidence decreases.
Ethnic Origin
Women of color have been found to be more prone to develop fibroids than Caucasians. Fibroids in colored women were also found to be larger and appear at an earlier age than in Caucasian women.
Obesity
The relationship between obesity and the development of fibroids is uncertain, although several researches have shown that obesity increases the likelihood of developing uterine fibroids.
No pregnancy or childbirth
Studies have shown that pregnancy and childbirth are preventive factors that protect against uterine fibroids.
Uterine fibroid types
The size of fibroids varies greatly among women, as some suffer from a large fibroid that can take in the entire abdominal area some have fibroids that are the size of a pill.
The development or growth of uterine fibroids is associated with changes in estrogen hormone, The more estrogen is secreted the larger the chances that uterine fibroids develop and grow.
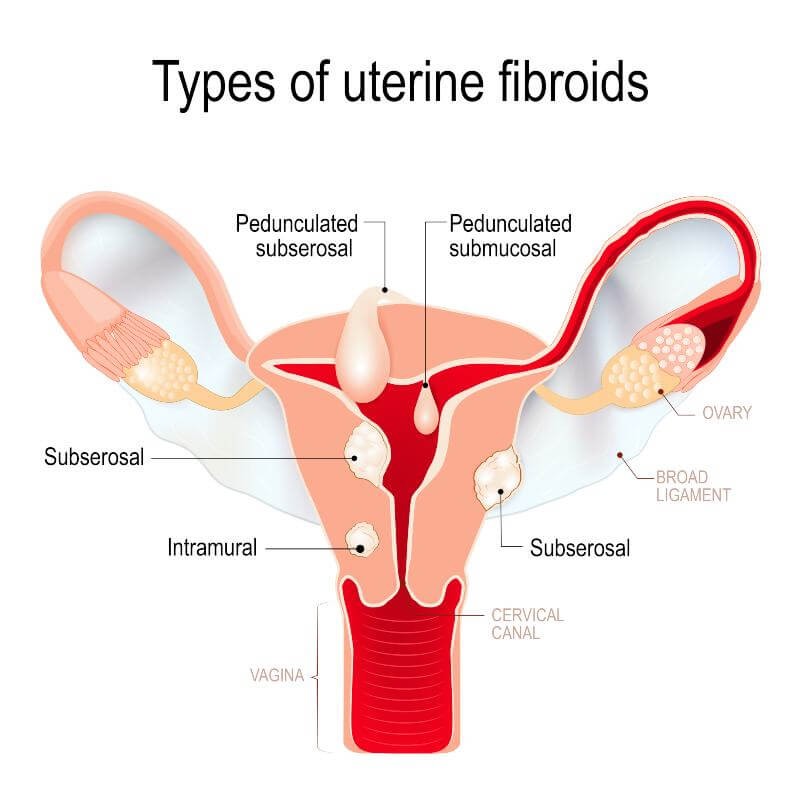
The types of uterine fibroids can be divided into 4 types, as follows:
1- Intramural fibroids these grow within the muscular uterine wall
This type of tumor increases the amount of menstrual blood loss and causes more discomfort or pain during menstruating. It can also decrease pregnancy chances due to it engorging the cavity. The severity of its symptoms and if it affects female fertility should be assessed by an OBGYN doctor that will decide if it can be treated conservatively or treatment steps taken.
2- Submucosal fibroids bulge into the uterine cavity
This type of tumor may cause difficulty in reproduction, recurrent miscarriage, as well as severe bleeding during menstruation, severe pain, and prolonged menstrual duration.
3- Subserous fibroids grow on the outer wall of your uterus (serosa).
These are the most common fibroid type they can push outside of the uterus and grow fast. They do not affect the endometrium lining or the menstrual cycle much but can press on other pelvic or abdominal organs causing pain and discomfort.
4- Pedunculated fibroids are subserous fibroids that develop a stem
This type of fibroid differs from the subserous fibroids only by it having a stem. This fibroid type can grow inside or outside the uterus.
Uterine Fibroids treatment
There is no medication that can help reduce the size of a fibroid mass permanently but Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists block estrogen and progesterone production that as previously discussed are factors that play a role in the development and growth of fibroids.
A myomectomy (surgical removal of fibroids) while preserving the uterus is the best treatment option for women that still want to have children. Depending on the location and size of the fibroid a myomectomy can be done through a laparotomy, laparoscopically and by a hysteroscope. All three approaches require general anesthesia, and your gynecologist will discuss which of the three options is best for your condition and why.
Radiofrequency ablation uses heat generated from an alternating current to accurately shrink or burn the fibroid.
Endometrial ablation is a “symptom” treating surgical procedure where the endometrium lining is removed or destroyed to treat heavy menstrual cycles. This treatment is not commonly used and especially not in women who want to still have children.
Uterine fibroids and pregnancy
Fibroids do not hinder fertilization or pregnancy occurring. However, fibroids especially submucous fibroids can be a factor in infertility or pregnancy loss.
Fibroids may also increase the risk of certain pregnancy complications, such as placental detachment, restricted fetal development, and premature birth.
It is important to know the exact location and sort of fibroid you are dealing with if pregnant or wanting to become pregnant to anticipate which steps should be taken to prevent the fibroid from causing complications.